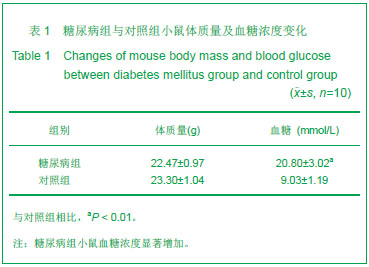
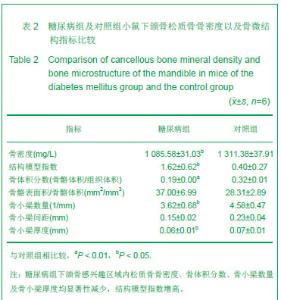
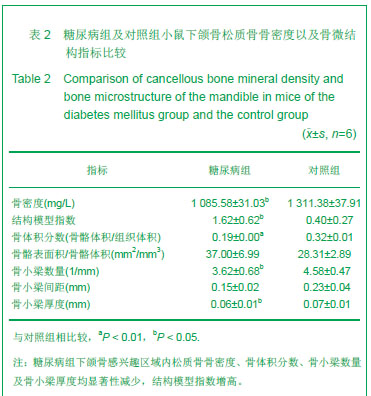
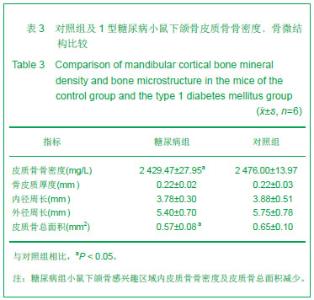
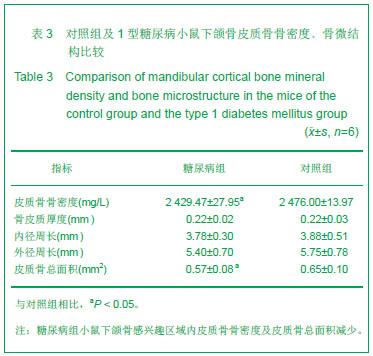
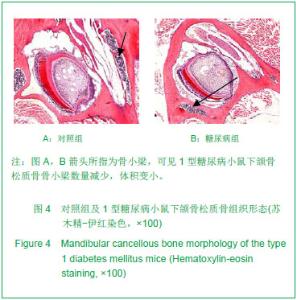
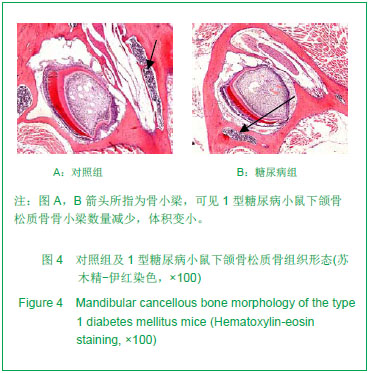
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (28): 5101-5107.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.28.001
Three-dimensional structure and morphology of the mandible in type 1 diabetes mellitus mice
Zhang Jun1, Jiang Li-ting1, Wang Jin-shen2, Zhou Qi2, Gao Yi-ming1
- 1Department of Stomatology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China;
2Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Shanghai 200025, China
-
Online:2013-07-09Published:2013-07-09 -
Contact:Gao Yi-ming, M.D., Department of Stomatology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China drgaoym@yahoo.com.cn -
About author:Zhang Jun, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China zjjz11071@gmail.com -
Supported by:Medical Guiding Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Committee, No. 114119a3500*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jun, Jiang Li-ting, Wang Jin-shen, Zhou Qi, Gao Yi-ming1. Three-dimensional structure and morphology of the mandible in type 1 diabetes mellitus mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(28): 5101-5107.
share this article
| [1]Motyl K, McCabe LR. Streptozotocin, type I diabetes severity and bone. Biol Proced Online. 2009;11:296-315. [2]Motyl KJ, Botolin S, Irwin R, et al. Bone inflammation and altered gene expression with type I diabetes early onset. J Cell Physiol. 2009;218(3):575-583.[3]Shyng YC, Devlin H, Sloan P. The effect of streptozotocin- induced experimental diabetes mellitus on calvarial defect healing and bone turnover in the rat. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001;30(1):70-74.[4]Pepelassi E, Xynogala I, Perrea D, et al. Histometric assessment of the effect of diabetes mellitus on experimentally induced periodontitis in rats. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2012;14(2):35-41. [5]Gomes DA, Spolidorio DM, Pepato MT, et al. Effect of induced diabetes mellitus on alveolar bone loss after 30 days of ligature-induced periodontal disease. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2009;11(2):188-192.[6]Okamoto M, Sato T, Shirai H, et al. A histomorphometric analysis on bone dynamics in denture supporting tissue under continuous pressure in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. J Oral Rehabil. 2001;28(6):553-559.[7]Zou C, Wang J, Wang S, et al. Characterizing the induction of diabetes in juvenile cynomolgus monkeys with different doses of streptozotocin. Sci China Life Sci. 2012;55(3): 210-218.[8]Chatzigeorgiou A, Halapas A, Kalafatakis K, et al. The use of animal models in the study of diabetes mellitus. In Vivo. 2009; 23(2):245-258.[9]Giglio MJ, Lama MA. Effect of experimental diabetes on mandible growth in rats. Eur J Oral Sci. 2001;109(3):193-197.[10]Duarte VM, Ramos AM, Rezende LA, et al. Osteopenia: a bone disorder associated with diabetes mellitus. J Bone Miner Metab. 2005;23(1):58-68.[11]Thrailkill KM, Liu L, Wahl EC, et al. Bone formation is impaired in a model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54(10): 2875-2881.[12]Bellenger J, Bellenger S, Bataille A, et al. High pancreatic n-3 fatty acids prevent STZ-induced diabetes in fat-1 mice: inflammatory pathway inhibition. Diabetes. 2011;60(4): 1090-1099. [13]Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, et al. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(7): 1468-1486. [14]Singh M, Detamore MS. Biomechanical properties of the mandibular condylar cartilage and their relevance to the TMJ disc. J Biomech. 2009;42(4):405-417. [15]Kuroda S, Tanimoto K, Izawa T, et al. Biomechanical and biochemical characteristics of the mandibular condylar cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(11):1408-1815.[16]Leidig-Bruckner G, Ziegler R. Diabetes mellitus a risk for osteoporosis? Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001;109 Suppl 2:S493-514.[17]Hamann C, Kirschner S, Günther KP, et al. Bone, sweet bone--osteoporotic fractures in diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8(5):297-305.[18]Unnanuntana A, Rebolledo BJ, Khair MM, et al. Diseases affecting bone quality: beyond osteoporosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(8):2194-206. [19]DiGirolamo DJ, Clemens TL, Kousteni S. The skeleton as an endocrine organ. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(11):674-683.[20]Mishima N, Sahara N, Shirakawa M, et al. Effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus on alveolar bone deposition in the rat. Arch Oral Biol. 2002;47(12):843-849.[21]Kunii R, Yamaguchi M, Aoki Y, et al. Effects of experimental occlusal hypofunction, and its recovery, on mandibular bone mineral density in rats. Eur J Orthod. 2008;30(1):52-56.[22]Shimomoto Y, Chung CJ, Iwasaki-Hayashi Y, et al. Effects of occlusal stimuli on alveolar/jaw bone formation. J Dent Res. 2007;86(1):47-51.[23]Verdelis K, Lukashova L, Atti E, et al. MicroCT morphometry analysis of mouse cancellous bone: intra- and inter-system reproducibility. Bone. 2011;49(3):580-587.[24]Layton MW, Goldstein SA, Goulet RW, et al. Examination of subchondral bone architecture in experimental osteoarthritis by microscopic computed axial tomography. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31(11):1400-1405.[25]Nishiyama KK, Campbell GM, Klinck RJ, et al. Reproducibility of bone micro-architecture measurements in rodents by in vivo micro-computed tomography is maximized with three-dimensional image registration. Bone. 2010;46(1): 155-161.[26]Jiang Y, Zhao J, Liao EY, et al. Application of micro-CT assessment of 3-D bone microstructure in preclinical and clinical studies. J Bone Miner Metab. 2005;23 Suppl:122-131.[27]Umoh JU, Sampaio AV, Welch I, et al. In vivo micro-CT analysis of bone remodeling in a rat calvarial defect model. Phys Med Biol. 2009;54(7):2147-2161.[28]Benhamou CL. Effects of osteoporosis medications on bone quality. Joint Bone Spine. 2007;74(1):39-47.[29]Abbassy MA, Watari I, Soma K. Effect of experimental diabetes on craniofacial growth in rats. Arch Oral Biol. 2008; 53(9):819-825.[30]Ogawa N, Yamaguchi T, Yano S, et al. The combination of high glucose and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) inhibits the mineralization of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells through glucose-induced increase in the receptor for AGEs. Horm Metab Res. 2007;39(12):871-875. [31]Okazaki K, Yamaguchi T, Tanaka K,et al. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), but not high glucose, inhibit the osteoblastic differentiation of mouse stromal ST2 cells through the suppression of osterix expression, and inhibit cell growth and increasing cell apoptosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2012; 91(4):286-296. [32]Holzhausen M, Garcia DF, Pepato MT, et al. The influence of short-term diabetes mellitus and insulin therapy on alveolar bone loss in rats. J Periodontal Res. 2004;39(3):188-193.[33]Coe LM, Zhang J, McCabe LR. Both spontaneous Ins2(+/-) and streptozotocin-induced type I diabetes cause bone loss in young mice. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(4):689-695. [34]Mc Cabe LR. Understanding the pathology and mechanisms of type I diabetic bone loss. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102(6): 1343-1357.[35]Botolin S, McCabe LR. Bone loss and increased bone adiposity in spontaneous and pharmacologically induced diabetic mice. Endocrinology. 2007;148(1):198-205.[36]Abbassy MA, Watari I, Soma K. The effect of diabetes mellitus on rat mandibular bone formation and microarchitecture. Eur J Oral Sci. 2010;118(4):364-369. [37]Gradin P, Hollberg K, Cassady AI, et al. Transgenic overexpression of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase is associated with induction of osteoblast gene expression and increased cortical bone mineral content and density. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196(1):68-81.[38]Sheng MH, Wergedal JE, Mohan S, et al. Targeted overexpression of osteoactivin in cells of osteoclastic lineage promotes osteoclastic resorption and bone loss in mice. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35280.[39]Phan TC, Xu J, Zheng MH. Interaction between osteoblast and osteoclast: impact in bone disease. Histol Histopathol. 2004;19(4):1325-1344.[40]Verhaeghe J, Thomsen JS, van Bree R, et al. Effects of exercise and disuse on bone remodeling, bone mass, and biomechanical competence in spontaneously diabetic female rats. Bone. 2000;27(2):249-256. |
| [1] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [2] | Wei Yuanbiao, Guo Huizhi, Zhang Shuncong. Finite element analysis of cortical bone trajectory screw fixation on adjacent segments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2799-2804. |
| [3] | Guo Xuan, Xie Jun, Suo Jinrong, Li Yingrui, Huang Lei, Ma Munan, Li Jingjing, Fu Songtao. Transplantation of islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 78-83. |
| [4] | Xu Guofeng, Li Xuebin, Tang Yifan, Zhao Yin, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun. The role of autophagy in ossification of the human ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181. |
| [5] | Wang Weijun, Liu Jie, Liu Jun, Jia Zhengbin, Fan Ruoxun. Simulation accuracy of cortical bone fracture based on different types of strain criterion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3828-3833. |
| [6] | Wu Dalei, Zhou Shouheng, Yan Jianwei, Li Bo, Xu Nuo, Shi Chun, Gao Yang. Alcohol extract of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. promotes bone healing in rats with periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3685-3689. |
| [7] | Yang Xiaoye, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Zhang Shuangyuan. Changes of bone mineral density and related factors during maxillary teeth occlusion after tooth extraction in diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 242-247. |
| [8] | Zong Zhiguo, Liu Su, Ma Pengpeng, Zhang Xin, Li Wei, Su Feng, Zhang Chunlin, Guo Jianwen, Wen Yi. Mechanical stability of the fracture at the junction of lumbar vertebral body and pedicle after implantation with different diameters of pedicle screws [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2794-2798. |
| [9] | Qin Haikuo, Luo Shixing. Correlation of cortical bone thickness and X-ray gray value in different planes of proximal femur with brittle fracture of female hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2867-2872. |
| [10] |
Wang Ning, Cui Tingting, Li Yongqi, Zhao Binbin, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu.
Autologous cortical bone block for repair of implant-site jaw bone defects
|
| [11] | Liu Jin, Gao Lilan, Peng Yulin, Zhang Xizheng. Mechanical properties of rat tibia under high-G environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1654-1658. |
| [12] | Song Xudong, He Yunwu, Li Yonglin, Chen Jing, Hu Junlan. Ultrasound-guided paravertebral nerve block for zoster-associated pain: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1797-1804. |
| [13] | Luo Xujiang, Xian Hai, Peng Liqing, Shen Shi, Zhang Bin, Gao Chao, Wang Zhenyong, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Han Gang, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Extraction of porcine cancellous bone by supercritical carbon dioxide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1508-1514. |
| [14] | Shao Yijie1, Jiang Huaye1, Gao Chao1, Luo Zongping2, Yang Huilin1. Effect of reduction of mechanical loading on subchondral bone and articular cartilage of early osteoarthritis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5611-5618. |
| [15] | Zhong Qiusheng1, Xia Weichao1, Guo Meizhen1, Zhu Haiqing1, Zhong Cuiqiong1, Shao Jieqi1, He Xiaohong2, Chen Xiumin2. Sandwiched Moxibustion plus Bushen Quhan recipe for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5670-5675. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||